[version_1.0]
The exercises in this course will have an associated charge in your AWS account. In this exercise, you will create the following resources:
Amazon CloudWatch Logs
The final task in this exercise includes instructions to delete all the resources that you create.
Familiarize yourself with DynamoDB pricing, Amazon SQS pricing, Amazon SNS pricing, Lambda pricing, API Gateway pricing, CloudWatch Logs pricing, and the AWS Free Tier.
This exercise provides you with instructions for how to build a proof of concept for a serverless solution in the AWS Cloud.
Suppose you have a customer that needs a serverless web backend hosted on AWS. The customer sells cleaning supplies and often sees spikes in demand for their website, which means that they need an architecture that can easily scale in and out as demand changes. The customer also wants to ensure that the application has decoupled application components.
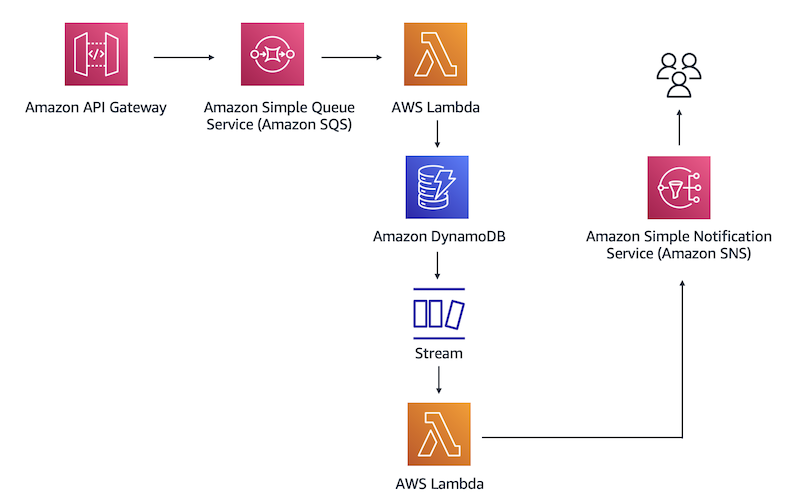
The following architectural diagram shows the flow for the serverless solution that you will build.

In this architecture, you will use a REST API to place a database entry in the Amazon SQS queue. Amazon SQS will then invoke the first Lambda function, which inserts the entry into a DynamoDB table. After that, DynamoDB Streams will capture a record of the new entry in a database and invoke a second Lambda function. The function will pass the database entry to Amazon SNS. After Amazon SNS processes the new record, it will send you a notification through a specified email address.
In this exercise, you will learn how to do the following:
Notes:
To complete the instructions in this exercise, choose the US East (N. Virginia) us-east-1 Region in the navigation pane of the AWS Management Console.
The instructions might prompt you to enter your account ID. Your account ID is a 12-digit account number that appears under your account alias in the top-right corner of the AWS Management Console. When you enter your account number (ID), make sure that you remove hyphens (-).
When you first create an account on AWS, you become a root user, or an account owner. We don’t recommend that you use the account root user for daily operations and tasks. Instead, you should use an IAM user or IAM roles to access specific services and features. IAM policies, users, and roles are offered at no additional charge.
In this task, you create custom IAM policies and roles to grant limited permissions to specific AWS services.
Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
In the search box, enter IAM.
From the results list, choose IAM.
In the navigation pane, choose Policies.
Choose Create policy.
The Create policy page appears. You can create and edit a policy in the visual editor or use JSON. In this exercise, we provide JSON scripts to create policies. In total, you must create four policies.
In the JSON tab, paste the following code:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:DescribeTable"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}This JSON script grants permissions to put items into the DynamoDB table. The asterisk (*) indicates that the specified actions can apply to all available resources.
Choose Next: Tags and then choose Next: Review.
For the policy name, enter Lambda-Write-DynamoDB.
Choose Create policy.
After you create the Lambda-Write-DynamoDB policy, repeat the previous steps to create the following policies:
A policy for Amazon SNS to get, list, and publish topics that are received by Lambda:
Lambda-SNS-PublishA policy for Lambda to get records from DynamoDB Streams:
Lambda-DynamoDBStreams-ReadA policy for Lambda to read messages that are placed in Amazon SQS:
Lambda-Read-SQSBecause AWS follows the principle of least privilege, we recommend that you provide role-based access to only the AWS resources that are required to perform a task. In this step, you create IAM roles and attach policies to the roles.
In the navigation pane of the IAM dashboard, choose Roles.
Choose Next.
On the Add permissions page, select Lambda-Write-DynamoDB and Lambda-Read-SQS.
Choose Next
For Role name, enter Lambda-SQS-DynamoDB.
Choose Create role.
Follow the previous steps to create two more IAM roles:
Lambda-DynamoDBStreams-SNSAPIGateway-SQSIn this task, you create a DynamoDB table that ingests data that’s passed on through API Gateway.
In the search box of the AWS Management Console, enter DynamoDB.
From the list, choose the DynamoDB service.
ordersorderIDKeep the remaining settings at their default values, and choose Create table.
In this task, you create an SQS queue. In the architecture for this exercise, the Amazon SQS receives data records from API Gateway, stores them, and then sends them to a database.
In the AWS Management Console search box, enter SQS and from the list, choose Simple Queue Service.
On the Get started card, choose Create queue.
The Create queue page appears.
POC-Queuearn:aws:iam::<account ID>:role/APIGateway-SQS.arn:aws:iam::<account_ID>:role/Lambda-SQS-DynamoDBChoose Create queue.
In this task, you create a Lambda function that reads messages from the SQS queue and writes an order record to the DynamoDB table.
In the AWS Management Console search box, enter Lambda and from the list, choose Lambda.
POC-Lambda-1Lambda-SQS-DynamoDBChoose Create function.
If needed, expand the Function overview section.
Choose Add trigger.
For Trigger configuration, enter SQS and choose the service in the list.
For SQS queue, choose POC-Queue.
Add the trigger by choosing Add.
On the POC-Lambda-1 page, in the Code tab, replace the default Lambda function code with the following code:
Choose Deploy.
The Lambda code passes arguments to a function call. As a result, when a trigger invokes a function, Lambda runs the code that you specify.
When you use Lambda, you are responsible only for your code. Lambda manages the memory, CPU, network, and other resources to run your code.
POC-Lambda-Test-1SQSThe SQS template appears in the Event JSON field.
Save your changes and choose Test.
After the Lambda function runs successfully, the “Execution result: succeeded” message appears in the notification banner in the Test section. This means that the Lambda function sent a test message “Hello from SQS!” from the SQS template to the DynamoDB table.
In the AWS Management Console search box, enter DynamoDB and from the list, choose DynamoDB.
In the navigation pane, choose Explore items.
Select the orders database. Under Items returned, the orders table returns “Hello from SQS!” from the Lambda function test.
In this task, you enable DynamoDB Streams. A DynamoDB stream captures information about every modification to data items in the table.
In the DynamoDB console, in the Tables section of the navigation pane, choose Update settings.
In the Tables card, make sure that the orders table is selected.
Choose the Exports and streams tab.
In the DynamoDB stream details section, choose Enable.
For View type, choose New image.
Choose Enable stream.
After the Lambda function reads messages from the SQS queue and writes an order record to the DynamoDB table, DynamoDB Streams captures the primary key attributes from the record.
In this task, you create an SNS topic and set up subscriptions. Amazon SNS coordinates and manages delivering or sending messages to subscriber endpoints or clients.
In the AWS Management Console, search for SNS and choose Simple Notification Service.
On the Create topic card, enter POC-Topic and choose Next step.
In the Details section, keep the Standard topic type selected and choose Create topic.
On the POC-Topic page, copy the ARN of the topic that you just created and save it for your reference.
You will need the ARN for the SNS topic later in this exercise.
On the Subscriptions tab, choose Create subscription.
For Topic ARN, make sure that the box contains the ARN for POC-Topic.
To receive notifications, for Protocol, choose Email.
For Endpoint, enter your email address.
Choose Create subscription.
The confirmation message is sent to the email address that you specified.
After you receive the confirmation email message, confirm the subscription. If you don’t receive an email message within a few minutes, check the spam folder.
In this task, you create a Lambda function for the Lambda-DynamoDBStreams-SNS role. The second Lambda function uses DynamoDB Streams as a trigger to pass the record of a new entry to Amazon SNS.
In the AWS Management Console, search for and open AWS Lambda.
POC-Lambda-2This role grants permissions to get records from DynamoDB Streams and send them to Amazon SNS.
Choose Create function.
DynamoDB and from the list, choose DynamoDB.Keep the remaining default settings and choose Add.
In the Configuration tab, make sure that you are in the Triggers section and that the DynamoDB state is “Enabled.”
Choose the Code tab and replace the Lambda function code with the following code:
import boto3, json
client = boto3.client('sns')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
for record in event["Records"]:
if record['eventName'] == 'INSERT':
new_record = record['dynamodb']['NewImage']
response = client.publish(
TargetArn='<Enter Amazon SNS ARN for the POC-Topic>',
Message=json.dumps({'default': json.dumps(new_record)}),
MessageStructure='json'
)Note: In the function code, replace the TargetArn value with the ARN for the Amazon SNS POC-Topic. Make sure that you remove the placeholder angle brackets (<>).
Your ARN might look similar to the following: arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:<account ID>:POC-Topic.
Choose Deploy.
On the Test tab, create a new event and for Event name, enter POC-Lambda-Test-2.
For Template-optional, enter DynamoDB and from the list, choose DynamoDB-Update.
The DynamoDB template appears in the Event JSON box.
Save your changes and choose Test.
After the Lambda function successfully runs, the “Execution result: succeeded” message should appear in the notification banner in the Test section.
In a few minutes, an email message should arrive at the email address that you specified in the previous task.
Confirm that you received the subscription email message. If needed, check both your inbox and spam folder.
In this task, you create a REST API in Amazon API Gateway. The API serves as a communication gateway between your application and the AWS services.
In the AWS Management Console, search for and open API Gateway.
POC-APIChoose Create API.
On the Actions menu, choose Create Method.
Open the method menu by choosing the down arrow, and choose POST. Save your changes by choosing the check mark.
/<account ID>/POC-Queuearn:aws:iam::<account ID>:role/APIGateway-SQSSave your changes.
Choose the Integration Request card.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and expand HTTP Headers.
Choose Add header.
For Name, enter Content-Type
For Mapped from, enter 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
Save your changes to the HTTP Headers section by choosing the check mark.
Expand Mapping Templates and for Request body passthrough, choose Never.
Choose Add mapping template and for Content-Type , enter application/json
Save your changes by choosing the check mark.
For Generate template, do not choose a default template from the list. Instead, enter the following command: Action=SendMessage&MessageBody=$input.body in a box.
Choose Save.
In this task, you use API Gateway to send mock data to Amazon SQS as a proof of concept for the serverless solution.
In the API Gateway console, return to the POST - Method Execution page and choose Test.
In the Request Body box, enter:
Choose Test.
If you see the “Successfully completed execution” message with the 200 response in the logs on the right, you will receive an email notification with the new entry. If you don’t receive an email, but the new item appears in the DynamoDB table, troubleshoot the exercise instructions starting from after you set up DynamoDB. Ensure that you deploy all of the resources in the us-east-1 Region.
After API Gateway successfully processes the request that you pasted in the Request Body box, it places the request in the SQS queue. Because you set up Amazon SQS as a trigger in the first Lambda function, Amazon SQS invokes the function call. The Lambda function code places the new entry into the DynamoDB table. DynamoDB Streams captures this change to the database and invokes the second AWS Lambda function. This function gets the new record from DynamoDB Streams and sends it to Amazon SNS. Amazon SNS, in turn, sends you an email notification.
In this task, you delete the AWS resources that you created for this exercise.
Congratulations! You have successfully completed the exercise.